As we step into the era of 5G technology, the question on everyone’s mind is: How does 5G technology enhance the Internet of Things (IoT)? This isn’t just a minor technological shift; it’s a monumental transformation that stands to redefine how we interact with the world around us. With speeds up to 100 times faster and remarkably lower latency, 5G is shaping up to be the backbone that IoT has been waiting for.
In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll dissect the intricate ways in which 5G technology enhances the Internet of Things. From healthcare to smart cities and beyond, we will explore how this powerful combination is paving the way for a more connected, reliable, and efficient future. Alongside the benefits, we’ll also delve into the challenges and complexities that this transformative technology brings, offering a balanced viewpoint on this groundbreaking evolution.
Table of Contents
What is 5G Technology?
In today’s interconnected world, cellular technology serves as the backbone for various forms of communication and data transfer. This is where 5G, or Fifth Generation, technology comes into play. As the successor to 4G LTE (Fourth Generation Long-Term Evolution), 5G aims to provide significant improvements in speed, latency, and overall performance. Let’s dive deeper into understanding what 5G technology is and how it’s designed to reshape not only our daily lives but also fuel advancements like the Internet of Things (IoT).
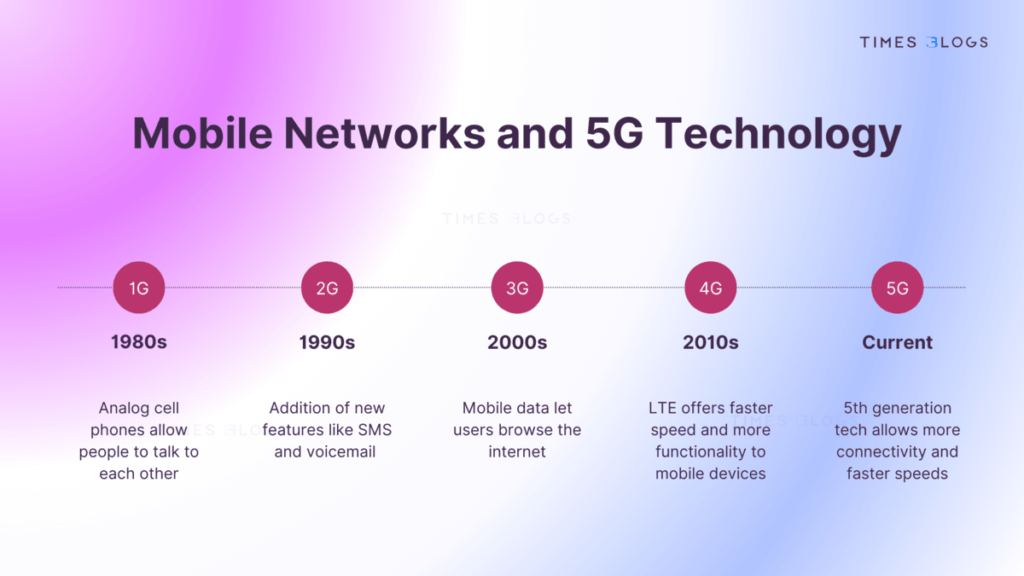
How is 5G Different from Previous Generations?
When considering 5G, it’s essential to understand how it compares to previous generations like 3G and 4G. Each generation brought specific improvements:
- 1G: Allowed analog voice calls.
- 2G: Introduced digital voice and SMS.
- 3G: Brought mobile data and internet browsing.
- 4G LTE: Increased data speeds and started the trend toward IP-based voice and data transmission.
5G is designed to be a substantial upgrade over these technologies, enabling ultra-high-speed data transmission with very low latency, thereby facilitating real-time communication and massive IoT applications.
Key Features of 5G:
To shed light on the central question of this blog—How Does 5G Technology Enhance the Internet of Things?—it’s essential to first explore the key features of 5G. These specific attributes act as the backbone for 5G’s role in boosting IoT capabilities. Let’s take a closer look
1. Ultra-high-speed data transmission
One of the headline features of 5G is its speed. While 4G LTE offers download speeds of up to 100 Mbps, 5G aims to deliver data rates that are 100 times faster. This leap in speed can revolutionize how we consume content, make real-time 4K video streaming possible, and even enable downloading entire movies in just seconds.
2. Low Latency
Latency refers to the delay between sending and receiving data. 5G aims to reduce this to as low as 1 millisecond, which is almost real-time. Lower latency is crucial for applications requiring immediate response, such as autonomous vehicles, real-time gaming, and remote surgeries.
3. Capacity to Connect a Multitude of Devices
5G technology uses more advanced radio technologies and network architectures to allow a higher volume of devices to be connected to the network simultaneously. This is particularly important for IoT applications where you might have hundreds or thousands of sensors and devices interacting in real time.
4. Enhanced Security Protocols
As we move towards an era where virtually everything will be connected to the internet, security becomes a paramount concern. 5G networks incorporate advanced encryption and data integrity checks to enhance security, thereby making it more difficult for unauthorized users to access the network or data.
5. Improved Energy Efficiency
One less discussed but equally important feature of 5G is its focus on energy efficiency. The network is designed to be smarter about sending signals, ensuring that it uses the least amount of energy to transfer data. This is crucial for battery-powered IoT devices, which need to operate for extended periods without frequent recharging.
5G technology is more than just an incremental upgrade over its predecessors; it’s a revolutionary step forward that promises to change how we interact with technology and the world around us. Whether it’s streaming content at breakneck speeds, driving autonomous cars, or managing smart cities, 5G is set to become the new standard for wireless communication. Most importantly, its improvements in speed, latency, capacity, security, and energy efficiency make it a cornerstone technology for powering the next generation of IoT applications.
The Internet of Things (IoT) Explained
In an age of rapid technological progress, the Internet of Things (IoT) stands as one of the most revolutionary concepts that promise to reshape how we live, work, and interact with our environment. Often seen as the future of technology, IoT refers to a complex network of smart devices connected to the internet, exchanging data to make our lives more efficient and convenient. However, what does this really mean, and how does it work? Let’s break it down.
What Makes Up the IoT Ecosystem?
The Internet of Things is not just a single technology or application; rather, it’s an ecosystem made up of several components, including:
- Devices: The most visible part of IoT, these are the physical objects equipped with sensors, software, and other technologies to collect and transmit data. Examples include smart thermostats, wearables, and connected vehicles.
- Connectivity: This entails the technologies that allow these devices to connect to the internet and to each other. It could be via Wi-Fi, cellular networks like 5G, or other specialized protocols like Zigbee or LoRaWAN.
- Data Processing and Storage: Once the data is collected, it needs to be sent to a cloud service or a data center where it is processed. Sophisticated algorithms analyze the data to derive insights or to inform decisions.
- User Interface: Finally, there are usually applications or dashboards where the collected data and insights are presented to the end-user. These interfaces can also allow users to control their IoT devices remotely.
Types of IoT Devices
- Consumer IoT: This includes devices like smart home appliances, wearable fitness trackers, and personal assistants like Amazon’s Alexa.
- Commercial IoT: Used in industries like healthcare and logistics for things like asset tracking, patient monitoring, and supply chain management.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Focuses on industrial applications such as predictive maintenance of machinery, energy management, and quality control in manufacturing.
- Smart Cities: IoT applications are increasingly being used to create smarter urban environments, with uses ranging from smart traffic lights to waste management systems.
Why Connectivity Matters
For the Internet of Things to function optimally, a strong, reliable, and fast network connection is vital. This is why the advent of 5G is so significant. With its ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and ability to connect a multitude of devices simultaneously, 5G serves as the perfect enabler for IoT applications.
Data Storage and Analytics
Data is often called the “new oil,” and in the case of IoT, this is absolutely true. The value of IoT comes from the data it collects and what you can do with that data. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms sift through the enormous volumes of data to identify patterns, make predictions, and generate actionable insights.
The Power of Real-time Data
One of the most powerful features of the IoT is its ability to provide real-time information. For instance, in an industrial setting, IoT sensors can monitor machinery in real-time, predicting failures before they happen and saving both time and resources.
The Internet of Things is a complex yet incredibly promising landscape that is already starting to affect various aspects of our lives. Whether it’s simplifying tasks in our homes, making businesses more efficient, or even revolutionizing entire industries, the potential is staggering. Its efficacy, however, relies on a robust infrastructure of connectivity, data storage, and data analytics. As we move toward a world where everything is interconnected, understanding the basics of the IoT ecosystem becomes crucial for anyone looking to keep pace with the next wave of digital transformation.
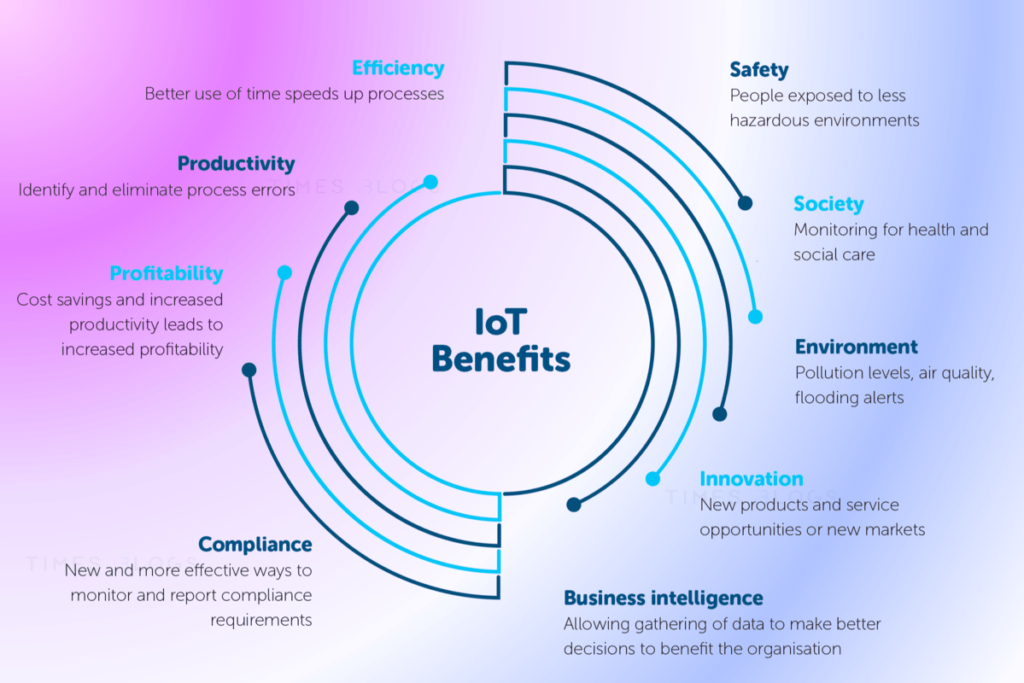
How Does 5G Technology Enhance the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The intersection of 5G technology with the Internet of Things (IoT) is like a harmonious symphony of speed, efficiency, and transformative capabilities. The union promises to redefine the technological landscape, adding new dimensions to IoT that were previously thought to be in the realm of science fiction. But how exactly does 5G technology enhance the Internet of Things? Let’s break it down.
Increased Speed and Efficiency
The high data rates that 5G technology brings to the table are a game-changer for IoT devices. Speeds of up to 20 Gbps mean that these devices can transfer large amounts of data in the blink of an eye. In practical terms, this kind of speed opens up avenues for more complex, data-intensive applications that were previously not feasible.
For example, in the realm of autonomous vehicles, high-speed data processing is absolutely crucial. The car’s onboard system needs to continuously analyze data from various sensors in real-time to make instantaneous decisions. A split-second delay could have catastrophic consequences. With 5G, data can be processed and decisions can be made in real-time, thus enhancing the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles.
Lower Latency
5G technology aims to offer latency as low as 1 millisecond, allowing for near-instantaneous communication between devices. This low latency is particularly impactful in applications that require real-time responses.
Take healthcare as an example. The concept of remote surgeries or telemedicine could become more viable with 5G technology. A surgeon could operate robotic arms to perform a procedure on a patient who is miles away, all in real-time, thanks to the low latency offered by 5G. Similarly, in industrial IoT settings, real-time data analytics and automated decision-making can optimize manufacturing processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Enhanced Capacity
One of the most significant advantages of 5G technology is its ability to handle a much larger number of connected devices compared to previous generations. This capability is crucial for IoT applications, especially in the context of Smart Cities. Here, you would have a plethora of devices such as traffic lights, weather stations, public transport systems, and emergency services all connected and sharing data.
With 5G’s increased capacity, these myriad devices can work in harmony without overwhelming the network, thereby enabling more seamless and intelligent urban living.
Improved Reliability
5G networks offer robust reliability features, including greater service availability and lower drop rates. This is invaluable for IoT applications where constant connectivity and data sharing are essential. Whether it’s tracking logistics, monitoring infrastructure, or ensuring patient health, a reliable network minimizes the risks of downtime and errors, which could otherwise lead to inefficiencies or even catastrophic failures.
Energy Efficiency
Last but not least, 5G technology is designed to be more energy-efficient. This is of critical importance in the IoT world, where many devices operate on battery power. Improved energy efficiency not only prolongs the lifespan of these devices but also makes them more sustainable in the long run. For example, environmental monitoring systems in remote locations can function for extended periods without requiring frequent battery replacements, thereby providing more consistent and reliable data.
Real-World Applications of 5G in IoT
The union of 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) promises a future that’s smarter, more efficient, and infinitely more connected. But how is this high-speed, low-latency technology already making a difference in our world today? Let’s delve into some real-world applications across various sectors.

Healthcare and IoT: A Life-Saving Fusion
When it comes to healthcare, time often equates to life. The fusion of 5G technology with IoT is creating a paradigm shift in how medical care is delivered, and in some cases, it’s proving to be life-saving.
Remote Surgeries
Traditionally, the idea of remote surgeries was hampered by latency issues, making it nearly impossible for a surgeon to operate with the precision and timeliness required. 5G, with its low latency, changes the equation entirely. Surgeons miles away can now control robotic arms in real-time, conducting delicate surgeries without any perceivable delay. For example, the first remote surgery was conducted in China, where a surgeon 200 miles away successfully removed a lab animal’s liver through a 5G-powered system. This feat could be a sign of how future surgeries will be conducted, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Real-Time Patient Monitoring
IoT devices like wearable health monitors have been around for a while, but they are bound by the limitations of data transfer speeds and network reliability. Enter 5G—With its ultra-fast speeds and rock-solid reliability, medical professionals can now get real-time updates on patients’ vital statistics. Think about a heart monitor that immediately alerts a cardiac team when a patient shows signs of an impending heart attack, enabling quick intervention that could save lives.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine isn’t new, but it’s being supercharged by the integration of 5G and IoT. High-definition video consultations are now smoother and more reliable, thanks to 5G’s enhanced speed and lower latency. This results in better patient-doctor interactions, leading to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. In rural or remote locations, where medical facilities are limited, this can be a game-changer.
Drug Management and Compliance
IoT-enabled medical dispensers connected via 5G can help healthcare providers track whether patients are taking their medications as prescribed. These smart dispensers release medicine only at predetermined times and alert healthcare providers if patients miss a dose. This technological alignment can be crucial for treating chronic conditions and ensuring successful post-operative recovery.

Smart Cities: The Future of Urban Living
Our cities are becoming increasingly congested, and the challenges associated with urban living—such as traffic, waste management, and public safety—are becoming more pressing. Smart Cities aim to address these issues through IoT, and 5G is the catalyst that could make these smart solutions extraordinarily effective.
Intelligent Traffic Management
In a 4G world, interconnected traffic management systems have shown promise, but they are still plagued by latency issues. 5G’s low latency and high data speeds make it possible for traffic lights, sensors, and cameras to communicate with each other almost instantaneously. For example, in some pilot projects, traffic lights automatically adjust their timings based on real-time traffic flow, reducing congestion and improving road safety.
Advanced Waste Management
Smart waste management systems are another crucial component of Smart Cities. Traditional waste collection routes can be highly inefficient, contributing to increased traffic and pollution. However, smart waste bins equipped with IoT sensors can communicate their fill levels in real-time via 5G networks. Cities like Seoul have already started using smart bins and have reported a reduction in collection costs by up to 83%, thanks to optimized routes and schedules.
Public Safety and Emergency Response
5G and IoT technologies can work in tandem to significantly improve public safety measures. For instance, connected security cameras can identify abnormal behaviors or suspicious packages and instantly alert authorities, speeding up emergency response times. IoT devices can also provide real-time data during natural disasters, guiding rescue efforts more effectively.
Sustainable Energy Management
5G can help cities become more sustainable by making energy consumption more efficient. Smart grids connected over 5G networks can monitor and analyze the energy usage patterns of an entire city, optimizing the distribution of electricity. Similarly, IoT sensors in public lighting systems can detect when and where lighting is needed, reducing unnecessary energy expenditure. Some cities have already adopted smart street lighting, saving up to 60% in energy costs.
Industrial IoT: Beyond Traditional Manufacturing
The convergence of 5G and IoT is setting the stage for a new era in manufacturing and industry. We’ve already discussed the efficiency and productivity gains, so let’s look at two other transformative applications:
Predictive Maintenance
In a traditional setting, equipment would often need to break down before being fixed, resulting in costly downtime. With 5G-powered IoT sensors, however, it’s possible to monitor equipment in real-time, catching issues before they escalate into serious problems. These predictive algorithms can forecast when a machine is likely to fail, allowing for preemptive maintenance that minimizes disruption and maximizes efficiency.
Augmented Reality (AR) for Training and Operations
The low latency and high data speeds of 5G make it possible to implement real-time Augmented Reality applications in industrial settings. For example, a new employee can wear AR glasses to get instant information and guidance while learning how to operate a complex machine, thereby reducing the learning curve and potential for error.

Agriculture: Smart Farming for a Sustainable Future
In the world of agriculture, the amalgamation of 5G and IoT technologies is being hailed as the dawn of ‘smart farming.’ Let’s explore two crucial applications that are changing the game:
Precision Irrigation
Traditional irrigation systems are often wasteful, overwatering some areas while neglecting others. With 5G-connected IoT sensors planted in the field, farmers can receive real-time information on soil moisture levels. These sensors can be integrated into automated irrigation systems that deliver water only where and when it’s needed, resulting in reduced water usage and improved crop yields.
Livestock Monitoring
The well-being of livestock is crucial for both ethical and economic reasons. IoT sensors can monitor various health parameters of animals, such as body temperature or movement patterns, and alert farmers to any abnormalities. 5G’s high-speed, low-latency capabilities ensure that this data is relayed in real-time, allowing for immediate intervention if an animal falls ill or is in distress.

Retail and Customer Experience: The Future of Shopping
In an age where online shopping is booming, brick-and-mortar retailers are leveraging the power of 5G and IoT to elevate the in-store experience and streamline operations. These technologies are bridging the digital-physical divide, offering new ways to engage customers and manage inventory.
Inventory Management
In the retail sector, 5G and IoT are facilitating better inventory management. Smart shelves fitted with IoT sensors can detect when stock is low or misplaced and can send instant alerts to the management system. This automated process leads to more efficient restocking and an overall improved customer experience.
Personalized Marketing
In physical stores, IoT sensors can track customer behavior—such as time spent in a particular aisle or interaction with a specific product. This data, collected and processed in real-time via 5G, can be used to deliver personalized marketing messages or deals to customers’ smartphones as they shop.
Education and Remote Learning: A New Frontier
As educational institutions grapple with the challenges and opportunities of the digital age, 5G and IoT are emerging as powerful tools for transforming learning experiences. Their combined capabilities promise to make remote learning more interactive and campus environments more secure and efficient.
Virtual Classrooms
5G could facilitate a truly immersive remote learning experience. With high data speeds and low latency, 5G makes real-time, high-definition video streaming seamless, enhancing the quality of virtual classrooms. Interactive and augmented reality-based learning experiences can also be incorporated to make remote learning more engaging.
Campus Safety
IoT devices, such as wearables equipped with GPS and biometric sensors, can be used to enhance student safety on campuses. These devices could send real-time data to security centers, enabling immediate action in emergency situations.
The potent combination of 5G technology and the Internet of Things is revolutionizing industries far and wide. In the domains of Industrial IoT and Agriculture, these innovations are contributing to more efficient systems, sustainable practices, and ultimately, a better future. As the coverage and capabilities of 5G networks continue to expand, we can expect even more disruptive changes that elevate our technological capabilities to new heights. Whether it’s in a factory, on a farm, in a hospital, or throughout an entire city, the enhanced IoT powered by 5G is setting the stage for unprecedented advancements.
Future Outlook
After exploring the real-world applications that answer our central question—How does 5G technology enhance the Internet of Things?—it’s time to turn our gaze toward the future. The marriage between 5G and IoT is just beginning, and the potential for transformative change is enormous.
The advent of 5G is expected to make edge computing more effective, thereby granting IoT devices the ability to undertake more complex, real-time analytics. This has implications for everything from smart cities becoming increasingly sustainable to healthcare systems utilizing more remote monitoring and telemedicine capabilities.
As we look forward, advancements in 5G security protocols will likely create more secure IoT ecosystems, fostering trust and broader adoption across both consumer and industrial landscapes.
In summary, the relationship between 5G and IoT seems destined for long-term impact, promising to revolutionize various aspects of our daily lives and the global economy. The question of how 5G technology enhances the Internet of Things will continue to unfold in exciting and innovative ways.
Challenges and Concerns: Navigating the Roadblocks
While 5G and IoT together offer an array of benefits across sectors, it would be remiss not to discuss the challenges and concerns that accompany this technological union. Here are some of the key issues that businesses, governments, and consumers must consider:
Security: A Double-Edged Sword
5G technology does offer enhanced security features, but the sheer scale of the Internet of Things makes the network potentially vulnerable. More devices mean more entry points for malicious activities. Security protocols within 5G aim to mitigate these risks, but as long as there is connectivity, there is potential for security breaches. Businesses and regulators will need to be ever-vigilant to protect against a new wave of sophisticated cyberattacks.
Cost: The Investment Dilemma
High-speed, low-latency networks don’t come cheap. Building the necessary infrastructure for 5G networks and setting up IoT devices can entail significant investment. This makes it difficult for smaller companies or economically challenged regions to readily adopt the technology. Over time, costs are likely to come down, but the initial financial barrier remains a significant concern for many.
Compatibility: The Challenge of Integration
The fast-paced evolution of technology often leaves older devices in the dust. This holds true for IoT devices as well, many of which may not be compatible with 5G networks. Upgrading to 5G may therefore require costly hardware updates or even total replacements, adding another layer of complexity and expense to the transition.
Data Privacy: Balancing Utility and Confidentiality
As IoT devices collect an increasing amount of data, questions arise about who owns this information and how it’s used. With 5G enabling more real-time data collection and analytics, the potential for misuse or unauthorized access to personal data is a significant concern. Regulatory frameworks may need to be adapted to ensure responsible data handling and protect consumer privacy.
Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating a Patchwork Landscape
The deployment of 5G and its integration with IoT often has to navigate a complex landscape of regulations. These can include building codes for installing new antennas, spectrum allocation, and even international agreements where data crossing borders is concerned. Differences in regulations among countries and regions can complicate the rollout of global 5G IoT solutions.
Environmental Impact: A Sustainable Future?
Although 5G technology promises greater energy efficiency, the environmental impact of deploying new infrastructure, such as antennas and servers, cannot be ignored. Furthermore, with the proliferation of IoT devices, electronic waste has become a concern. Sustainable design and recycling programs will become increasingly important as these technologies become more widespread.
Social and Ethical Implications: The Human Factor
The rush to adopt new technologies can sometimes overlook social and ethical considerations. For example, automation enabled by IoT and 5G could lead to job displacement in certain sectors. The digital divide could also widen if access to 5G technology is not equitable, exacerbating social inequalities.
The marriage of 5G and IoT technology is set to revolutionize the way we interact with the world around us. From healthcare and smart cities to industrial applications and beyond, the potential is truly exciting. However, this technological leap forward comes with its set of challenges—security, cost, compatibility, data privacy, regulatory complexities, environmental concerns, and social implications are just some of the hurdles to overcome. As we venture into this new frontier, it will require concerted efforts from all stakeholders to navigate these challenges effectively. The ultimate aim is to ensure that the vast potential of 5G and IoT benefits society as a whole while minimizing the risks and downsides.
Conclusion: Bridging the Future with 5G and IoT
In answering the question, “How does 5G technology enhance the Internet of Things?”, it becomes clear that the leaps made in speed, latency, capacity, reliability, and energy efficiency are pivotal. These 5G advancements are the catalysts transforming the landscape of IoT, touching every facet of human life from healthcare and urban living to industry and agriculture.
This synergy has already begun revolutionizing real-world applications, demonstrating the capability to make cities smarter, medical services more efficient, and industries more productive. The examples we explored—whether it’s the impact on healthcare through remote surgeries and real-time monitoring, or the creation of smarter, more sustainable cities—speak volumes about the transformative potential of this technology.
However, as we delve into this brave new world, it’s vital to recognize the challenges that lie ahead. Security concerns, cost implications, compatibility issues, and even ethical considerations must be thoughtfully addressed to harness the full power and potential of this technological marriage.
In conclusion, while hurdles do exist, the symbiotic relationship between 5G and IoT is poised to reshape our world, making it smarter, more efficient, and more connected. The task that remains is to navigate the challenges conscientiously to ensure that the promise of this innovation is realized to its fullest extent, benefiting society at large.
By understanding the nuances of how 5G enhances the Internet of Things, we can better prepare for a future that promises unprecedented opportunities, all while carefully navigating the complexities that such advancement entails.